Haptic simulation technology for Human-Product Interaction ? Haptic based resistance training machine
(HPRC: Human-Oriented Product Innovation Research Center):
This research is focusing on the issues of developing physical haptic simulators, and as an example of haptic simulators, resistance training machine that can implement a wide variety of resistance training is designed and controlled. This haptic simulator in this research can provide proper level of resistance and generate proper path for individual and protect the users from injuries. Programmed individual exercise with haptic simulator will be tested and compared for the effectiveness of this method.
Biomechanical background
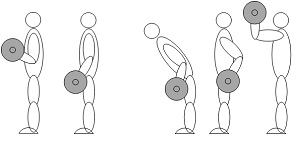
Resistance training that is representative health care has been shown to affect improvement of muscle power, strength, endurance as well as health promotion and muscle hypertrophy. But conventional exercise machines are difficult to be customized to each individual who has different levels of physical conditions and exercise ability. The important variables of resistance training are correct posture (fig 1.) and proper training load. The resistance training simulator in this research can provide proper level of resistance with respect to user¡¯s biomechanical behavior (fig 2.) and generate proper path during the motion.
Customized resistance training with the resistance training simulator
Resistance training simulator which is developed in this research has 3 components: 1) Training simulator 2) Main controller 3) Display panel console(fig 3.). We have applied impedance control scheme(fig 4.), thereby resistance training simulator allows users to exercise in a correct posture with respect to a pre-established individual database. To match the human strength curve (e.g. angle-torque relationship curve), we also offers different types of resistances which can vary over the range of motion. This adjustability is attained through static damper and computed torque control schemes including friction compensation with nonlinear parameter estimations of designed simulator.
References
- J. Park, K. Kim and D. Hong, "Variable impedance control of weight lifting simulator", IJCC workshop.120-124, 2008
- J. Park, K. Kim and D. Hong, ¡°Design and control of Haptic based resistance training simulator employing¡± KSPE conference, May. 2009
- J. Park, K. Kim and D. Hong, ¡°Haptic-based resistance training simulator employing impedance¡± KSPE conference, Oct.2009
- J. Park, K. Kim and D. Hong, ¡°Force control with nonlinear friction compensation of resistance simulator¡± KSPE conference, 2010